
Sanaa, Yemen — In his house on the outskirts of Yemen’s capital Sanaa, Mothafar squats on the floor, proudly displaying the pencil sketches made by his 21-year-old daughter, Emtenan, who sits silently beside him, dressed fully in black.
The drawings speak volumes. One shows a child curled up into a ball inside a deep hole in the ground, a lush tree sprouting out of them. Another depicts a man pulling a young girl away from a school building, to which she looks back with a devastated look on her face.
Emtenan has autism and finds it challenging to interact with others socially and typically avoids eye contact, her father explains. A therapist has been working closely with her to help her use sketches to express herself.
“Look at these drawings,” Mothafar said proudly. “She has so much talent and I’m sure there is so much more she can do. But given the situation we’re in… there is only so much I can give her,” the widower and father of five told CNN. He asked that he and his daughter be referred to only by their first names, because of the ignorance and stigma associated with autism in Yemen.
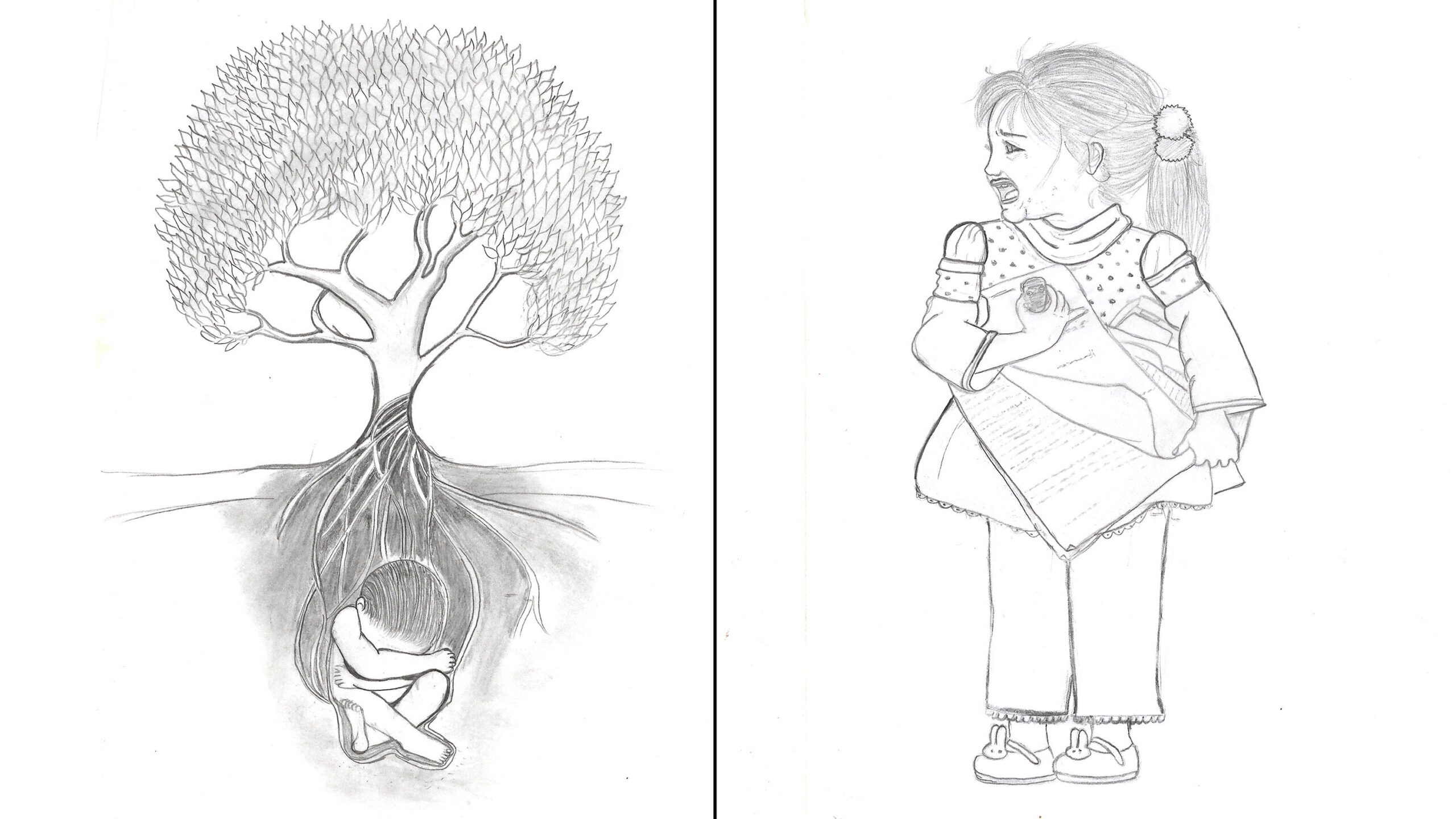

Emtenan, 21, who is autistic and largely non-verbal, works with a therapist who helps her use her drawings to communicate. Courtesy Emtenan
As a farmer with no formal education, Mothafar says he knew little about autism until he had Emtenan, and says he feels guilty for not spotting early signs of the condition.
“I thought she was only being a silly child,” he says, recalling her screaming fits, repetitive movements and inability to play with other children by the age of 4. “I didn’t know [what the condition was], and neither did anyone we knew.”
Being a woman with autism, Emtenan belongs to two marginalized groups in a country that has long ranked among the lowest globally for gender equality.
“Yemen’s society still regards women as objects that must be concealed and hidden,” said Afrah Nasser, Yemen researcher at Human Rights Watch. They face cultural and social barriers, such as restrictions on their movement, marriage choices and access to education. They are also subject to gender-based violence.
Women with autism face even greater challenges, due to the stigma and lack of awareness that persist around the condition. “By virtue of women facing more hardships than men in the various aspects of life, the plights of autistic women are multiple that of a man,” Nasser told CNN.
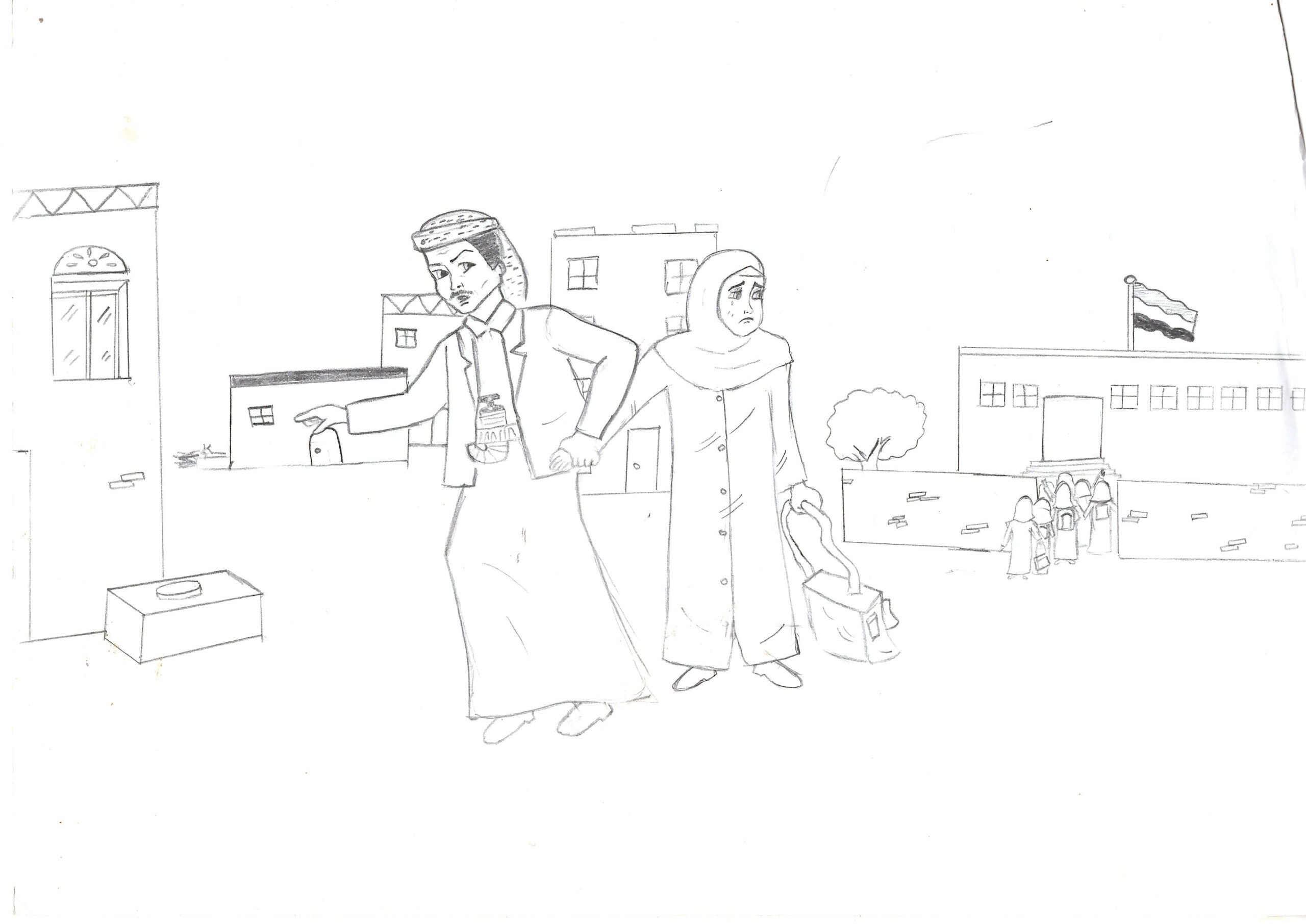
This pencil drawing shows a man pulling a young girl away from a school building, as tears roll down her face. Due to her autism, Emtenan struggled to settle down in school. Courtesy Emtenan
Autism spectrum disorder refers to “a broad range of conditions characterized by challenges with social skills… and communication, repetitive behaviors, resistance to changes in routine, or restricted interests,” according to Dr. Daniel Geschwind, professor of human genetics, neurology and psychiatry at UCLA.
There is wide variation in the type and severity of symptoms people experience and so therapies and interventions also vary and should be based on an individual’s needs. Early diagnosis enables early intervention and behavioral adjustment, which helps improve an autistic person’s condition and quality of life.
But in Yemen, spotting the signs of autism in a child is the family’s responsibility, Dr. Tameem Al-Basha, professor of special education at the Ibb University, told CNN, because the health sector has been destroyed by a civil war, which is entering its tenth year. The devastation has caused one of the world’s worst humanitarian crises and stripped many people with autism of the opportunity for diagnosis or treatment.
Rising costs in wartime a huge barrier to care
It was not until she turned 6 that Emtenan was diagnosed with autism. She spoke only a few words, had frequent tantrums, was hyperactive and would break things, Mothafar explained. School was also a struggle as she couldn’t settle well in class or follow simple instructions.
“No one advised us to visit a specialist. I would’ve done something [earlier],” added the 54-year-old, who says he now does everything he can to support his daughter.
But the treatment facilities closest to them charged exorbitant fees, he said, and the one he could afford was 22-km from their home. The journey there cost $8, triple what it did before the war. “Now, just thinking of the cost of transportation to make these trips, is exhausting,” he said.
Ultimately, Mothafar said he could not keep up. “After the war [began], things worsened greatly as the economic and security situation meant that I was less and less capable of giving her the care she needed,” he said. But his daughter’s behavior had been improving so their medical visits went down to twice a month, then monthly, and eventually stopped when Emtenan was 13. At that time, the war was already underway.
Conflict affected not just prices but also Emtenan’s temperament: “The sound of bombs and shelling also added to her agitation,” Mothafar told CNN.
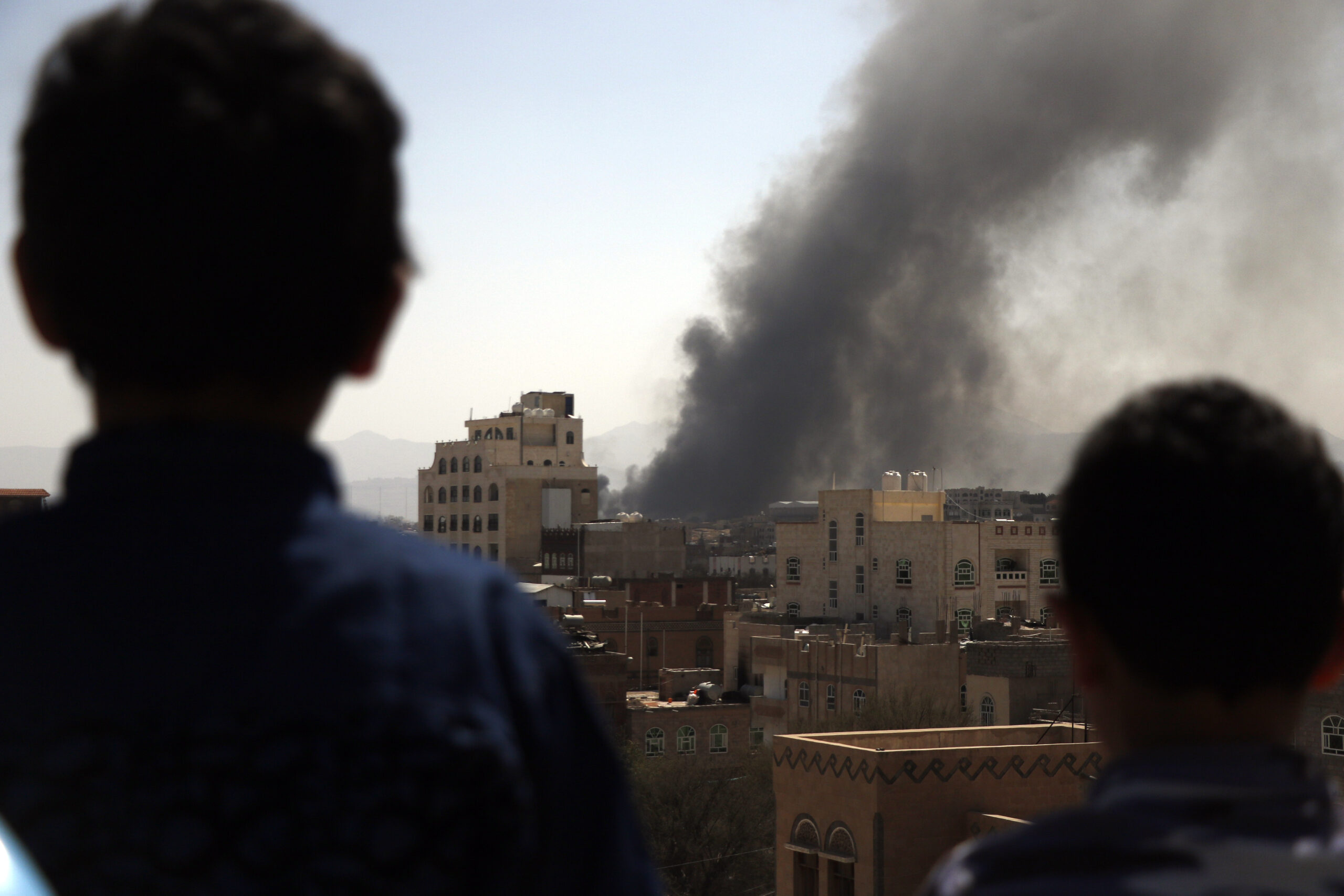

Children look on as smoke billows above the residential area following airstrikes of the Saudi-led coalition targeting Houthi-held military positions on March 07, 2021 in Sanaa, Yemen. Mohammed Hamoud/Getty Images
These days, a therapist visits Emtenan for a full day each month. At 5,000 Yemeni rials ($20 USD) a visit, that is all her father can afford, telling CNN he earns approximately 50,000 rials ($95) a month growing tomatoes, though his brother in Saudi Arabia sends about $50 a month to help.
“During these visits, she’s taught how to express and take care of herself, she’s also encouraged to do house chores and interact with others, and her surroundings. She’s responding well,” Mothafar said, though she still speaks in short sentences and doesn’t engage with her surroundings with ease.
A healthcare system itself on life support
The number of facilities still able to offer treatment is unknown, says Abdullah Bunyan, head of the independent National Union of Yemeni Disabled Associations. There were 118 organizations registered with the union before the war, but “we are unable to define the exact number of entities still able to offer support and treatment, due to the economic and security situation in Yemen,” he told CNN.
Nouriya Mishlen is the head of the independent People of Determination Foundation for Special Education in Sanaa, a center providing treatment and rehabilitation for people with special needs. As an independent entity, the center relies on donations, which dropped significantly when the war began. The four-room facility is run down; the furniture appears worn and in disrepair. In some classrooms, carpets and curtains are absent, and even some bathrooms lack functioning water pumps. The small garden outside is overgrown.
“In the past, our operating costs were affordable, including rent, electricity, water, and psychologist salaries,” Mishlen told CNN. “However, inflation and war have doubled the prices, and we are barely able to cover our operational costs.”
Human resources are equally low. According to 2016 figures from the World Health Organization, there are just 0.2 psychiatrists and 0.4 psychologists per 100,000 people in Yemen; in the US, this figure is 10.5 psychiatrists and 29.8 psychologists per 100,000 people.
Mothafar is grateful he’s found a reliable female therapist to assist Emtenan. “To have her taken care of here at home is ideal. I feel reassured that she’s safe, with another woman,” he explained. But having access to a carer doesn’t offer protection from society’s judgement.
"If she was a boy, it wouldn’t have been an issue. But she’s a girl. Her behavior has brought us scandal and shame"
Multiple studies show that families often suffer from negative societal responses to children with autism, especially when they exhibit socially inappropriate behaviors in public. For girls, this would include speaking loudly, yelling or screaming, aggressiveness, defiance and stubbornness, especially toward cultural norms like modest clothing or being quiet among men they are not familiar with.
“Some kids might face abuse, especially these days,” with the war and living conditions at their worst, said Fayad al-Derwish. The architect, who was born in 1990, grew up with autism in Yemen and faced bullying as a child.
According to al-Derwish, Oxfam’s Water and Sanitation Lead in Yemen, it is common for people in rural areas, home to around two-thirds of Yemen’s estimated 34 million people, to see the onset of autism as possession by a djinn, or devil. “If you have any health issue or psychological issue, the first thing the sheikh [local religious leader] in the village does is he brings a piece of steel, burns it with fire, and puts it on your stomach. If you go to a swimming pool in Yemen, you’ll see this mark on peoples’ stomachs,” said al-Derwish.
Dr. Sahar Taresh, senior lecturer at Malaysia’s Lincoln University College, researches awareness levels of autism in her home country of Yemen. Taresh said that while autistic people of both genders are subjected to abuse based on the belief their condition is caused by an evil spirit, “women are more prone to such treatment as a result of fear of being ‘loved by a djinn,’ and the possibility of her tarnishing her family’s reputation, or bringing them shame by her actions.”
Women have long faced discrimination and hostility in Yemen, which in turn affects their access to resources. For most years between 1998 and 2022, Yemen performed the worst on the United Nations’ Development Programme’s gender inequality index. This means that while, theoretically, both men and women have equal access to the same therapy opportunities for autism, family and society choose to “prioritize males over females,” said Adila Al-Khader, secretary-general of the Yemeni Women’s Union.
This gender inequality deepened, and the discrimination of Yemeni women worsened, as a result of the conflict. Destitution and displacement added to the many layers of vulnerability for girls and women, exposing them to more gender-based violence, particularly those with disabilities.
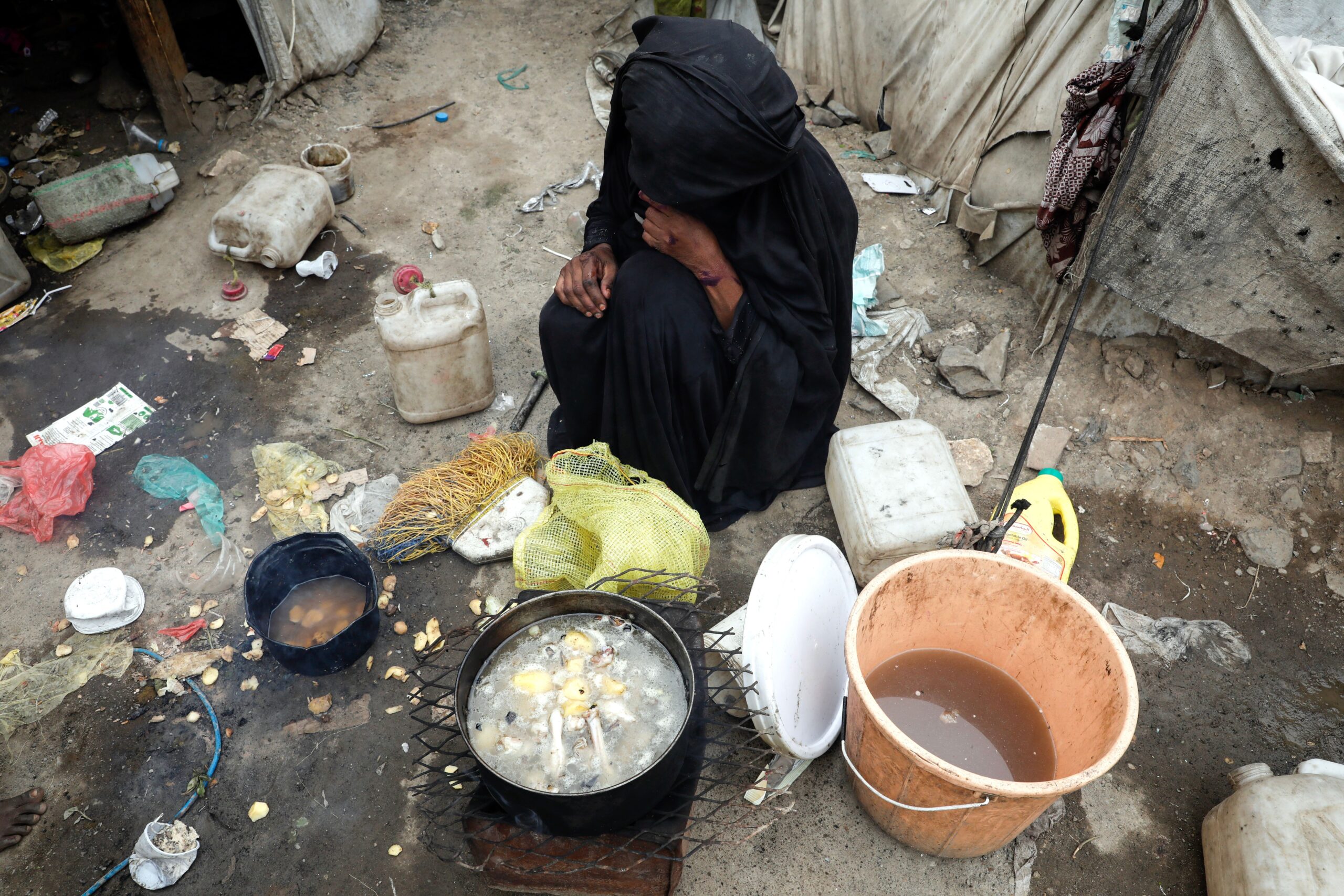

A Yemeni woman prepares food for her family outside a shelter at a makeshift camp for Internally Displaced Persons in Sanaa, Yemen, on August 22, 2023. Yahya Arhab/EPA-EFE/Shutterstock
‘Protecting her from herself’
Adel al-Yazidi’s 16-year-old daughter was diagnosed with autism and severe ADHD at the age of 5 and has trouble communicating and concentrating. While living in Saudi Arabia in 2020 she wandered out of her house and fell victim to a group of young men who sexually abused her.
Adel al-Yazidi, said he and his wife now chain the teen’s legs to her bed for most of the day to keep her at home, safe from sexual abuse. In a visit with a journalist, the girl showed no sign of upset over her restricted movement, cheerfully bouncing and interacting with her father.
“It’s to protect her from herself. I have no other choice,” said the father of three during a video call from Cairo, where the family is currently based. Her mother explained that they struggle to stop her daughter from wandering off.
“If she was a boy, it wouldn’t have been an issue. It wouldn’t have mattered what he does or does not do. He’d be able to fend for himself. But she’s a girl,” al-Yazidi said. “Her every action matters. And her behavior has brought us scandals and shame,” he added.
Khader, of the Yemeni Women’s Union, explained that many Yemeni families hide their autistic daughters because they know they won’t be embraced by society, or accepted as wives. “They are looked down upon and disrespected, and are therefore mistreated by their own families,” both verbally and physically, she said.
"I wish I could give her more. I want her to lead a life as normal as can be… I’ll do my best to help her achieve it"
A therapist in Sanaa, who asked not to be named due to the stigma associated with caring for women with autism, told CNN she’s seen marks of what she believed was beating and torture on a 16-year-old girl with autism. She added that such girls are often kept out of sight, and sometimes get married to grooms who aren’t told the truth about their condition, and are then left to their own fates, which could include marital abuse or divorce.
Khader, of the Yemeni Women’s Union, says that the biggest problem in Yemen lies with families’ lack of understanding of how to deal with girls growing up with autism. But she adds that increasing community awareness about this disorder will greatly contribute to reducing bullying and increasing the integration of this group into society and in their families.
“Training and qualifying women specialists in the field of autism spectrum, as well as creating specialized and free centers, will also [help] significantly.”
In the meantime, Mothafar refuses to give up on his daughter. They interact mostly with close friends and family who treat Emtenan’s condition with respect to avoid her facing any harassment or mistreatment, and Mothafar is careful to keep it that way. “It’s something I can’t tolerate if anyone refers to her condition in a mocking or bullying way,” he said.
“I wish I could give her more. I want her to lead a life as normal as can be, where she interacts with the world in a normal way, establishes relationships and completes her education… I’ll do my best to help her achieve it.”



