Share


1 of 6
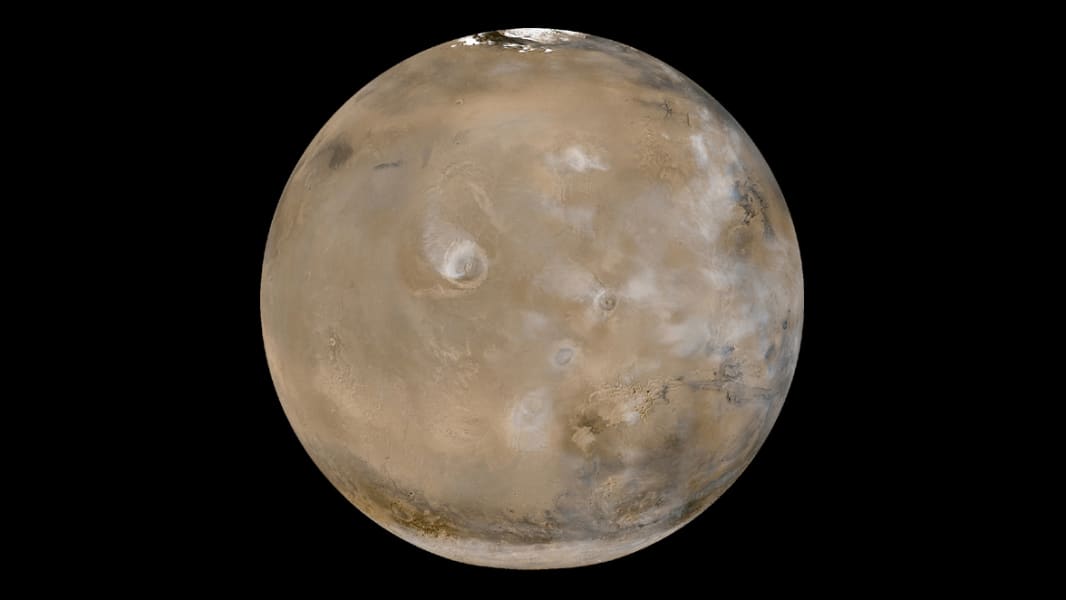
This view of Mars shows huge volcanoes in what's called the Tharsis Montes region. The photo is a composite of 24 images taken on February 14, 2003, by the Mars Global Surveyor, a NASA spacecraft orbiting the red planet. NASA says Tharsis Montes is the largest volcanic region on Mars. It's about 2,485 miles (4,000 kilometers) across and 6 miles (10 kilometers) high. It contains 12 large volcanoes, including Olympus Mons, the largest of the Tharsis volcanoes. JPL/NASA
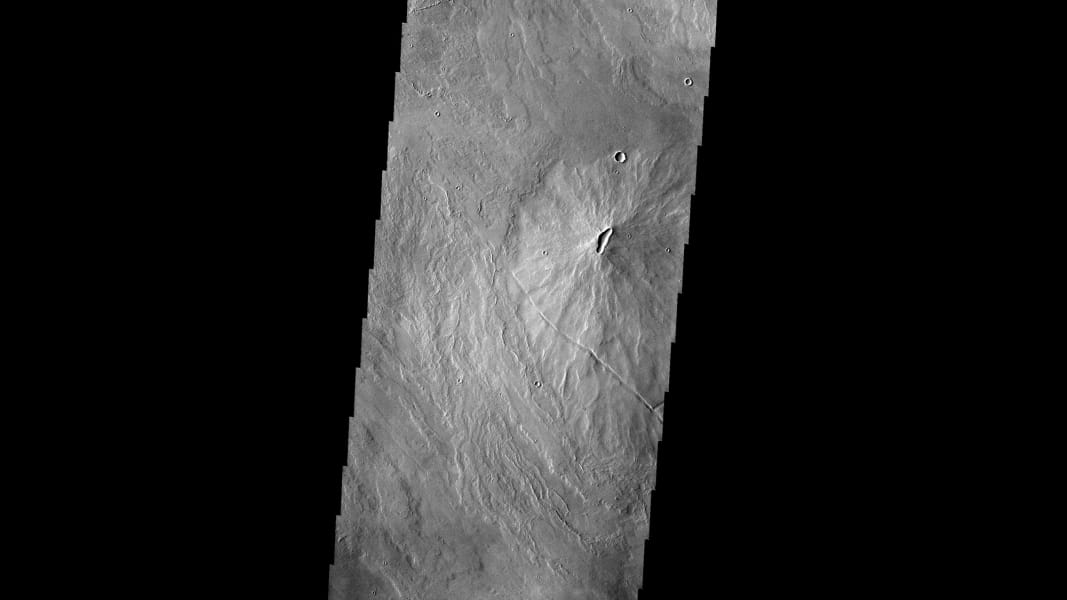
This image taken by the Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows volcanoes dotting the Martian landscape in the Tharsis region. JPL/NASA
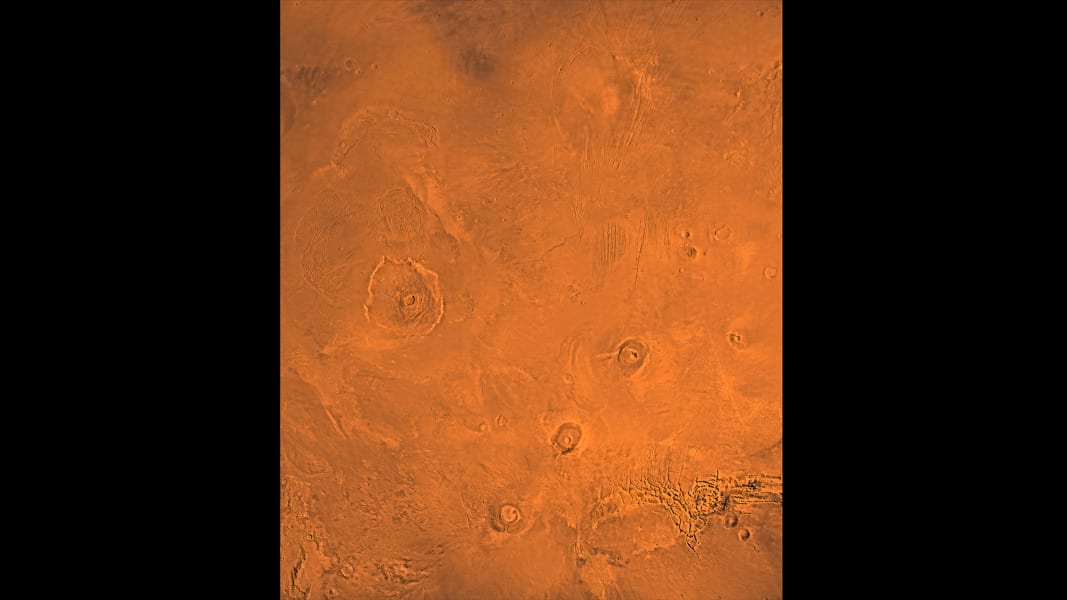
This image shows the Tharsis Bulge, a huge ridge on Mars covered by three large volcanoes (from lower left to right): Arsia, Pavonis and Ascraeus Mons. To the left is the huge Olympus Mons volcano. JPL/NASA
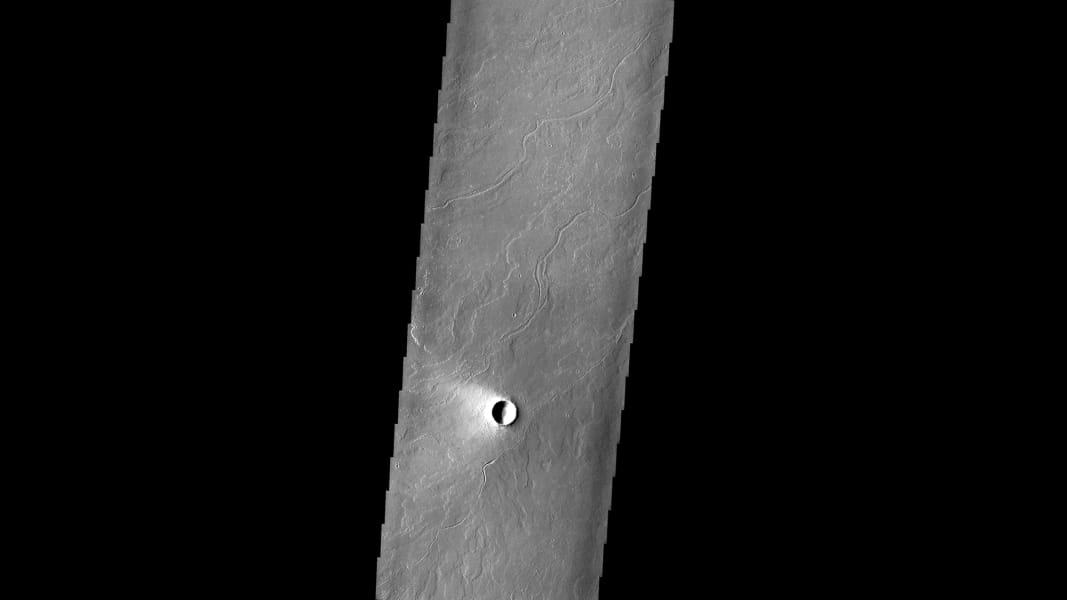
The area around the Olympus Mons volcano has lava flows, which appear as the lighter area near the volcano. JPL/NASA
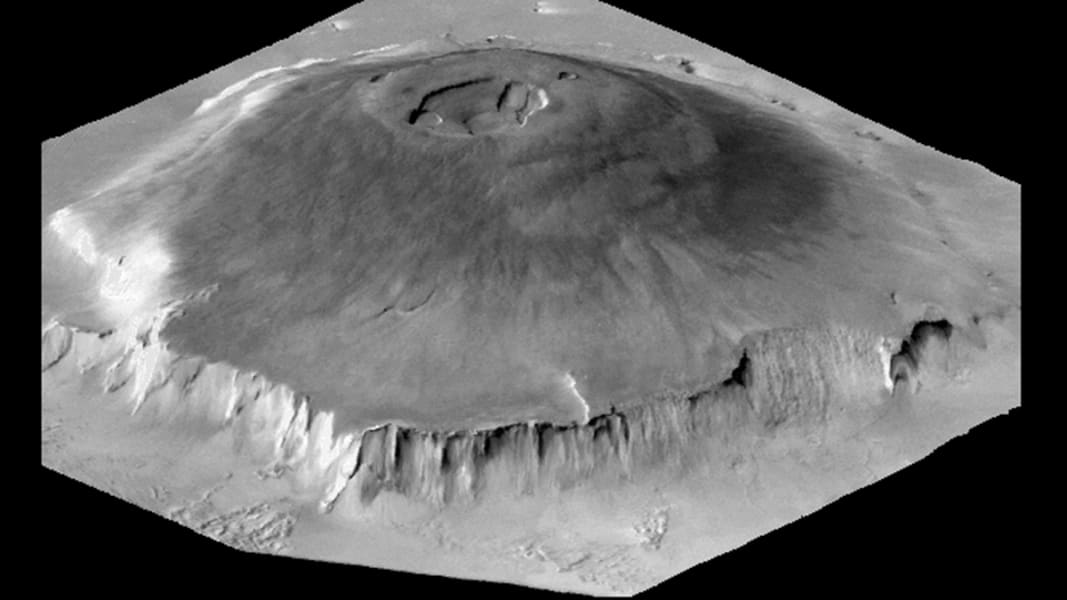
Olympus Mons in the Tharsis Montes region is largest known volcano in our solar system. JPL/NASA
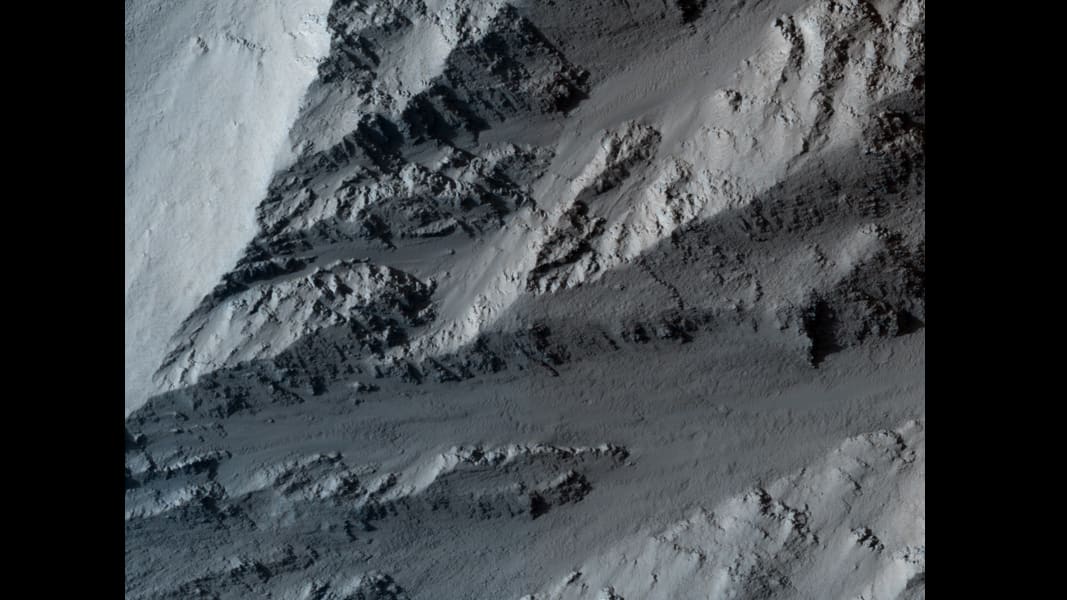
This image shows the northern edge of Olympus Mons on Mars. The cliff has hard layers of lava and soft layers that may be dust or volcanic ash. The image was taken by NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter on March 2, 2010. JPL/NASA